
Now if we graph our function on ordinary rectangular coordinate axes in GeoGebra, we get the following exponential curve. Setting up the Golden Spiral using GeoGebra
#Define golden spiral free#
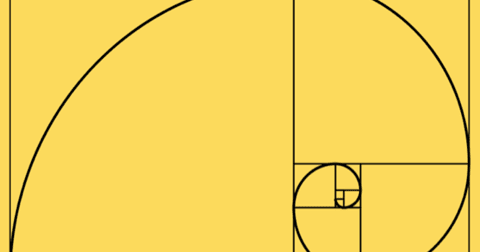
We'll use the excellent free graphing tool GeoGebra from here on. Using this value, and taking the simple case where a = 1, our function becomes: The Golden Spiral has the special property such that for every 1/4 turn (90° or π/2 in radians), the distance from the center of the spiral increases by the golden ratio φ = 1.6180.įor this to occur, cot b must take the value (which comes from solving our function): Note: Normally, we use θ for the independent variable, but we often use t as we can think of the spiral being traced out over time. We can write the general logarithmic spiral as a function in polar coordinates using t as follows: The Golden Spiral is a special case of the logarithmic spiral. Choosing the start point for the fern is not an exact science!) Golden Spiral (In an actual logarithmic spiral, they are exactly the same.
In the fern case above, b ≈ 1.4 radians (≈ 80°).Īs a consequence of the way we defined the logarithmic spiral, the ratio of the distances from the center to each spiral arm of an adjacent pair is constant.ĭistance to the first arm: distance to second armĭistance to the second arm: distance to third arm So the coordinates of a point on the curve in polar coordinates is given by ( r, θ).ī is the angle (in radians - the "equal" angle) that the line from the center of the spiral makes with the tangent to the spiral. Θ is the angle (in radians) from the horizontal axis. R is the distance from the origin (or "pole") The formula for a logarithmic spiral using polar coordinates is:
Otherwise, if we use ordinary rectangular coordinates, the formulas become very complex. We normally use functions in Polar Coordinates when describing spirals. To see what this means, the 3 acute angles marked in the following fern image are approximately 80° This is why they are also known as "equi-angular" spirals. Logarithmic spirals grow such that the angle of a line from the center of the spiral to the tangent to the curve at that point is constant.

The Golden Spiral that Pehr is asking about is a special case of the logarithmic spiral.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
